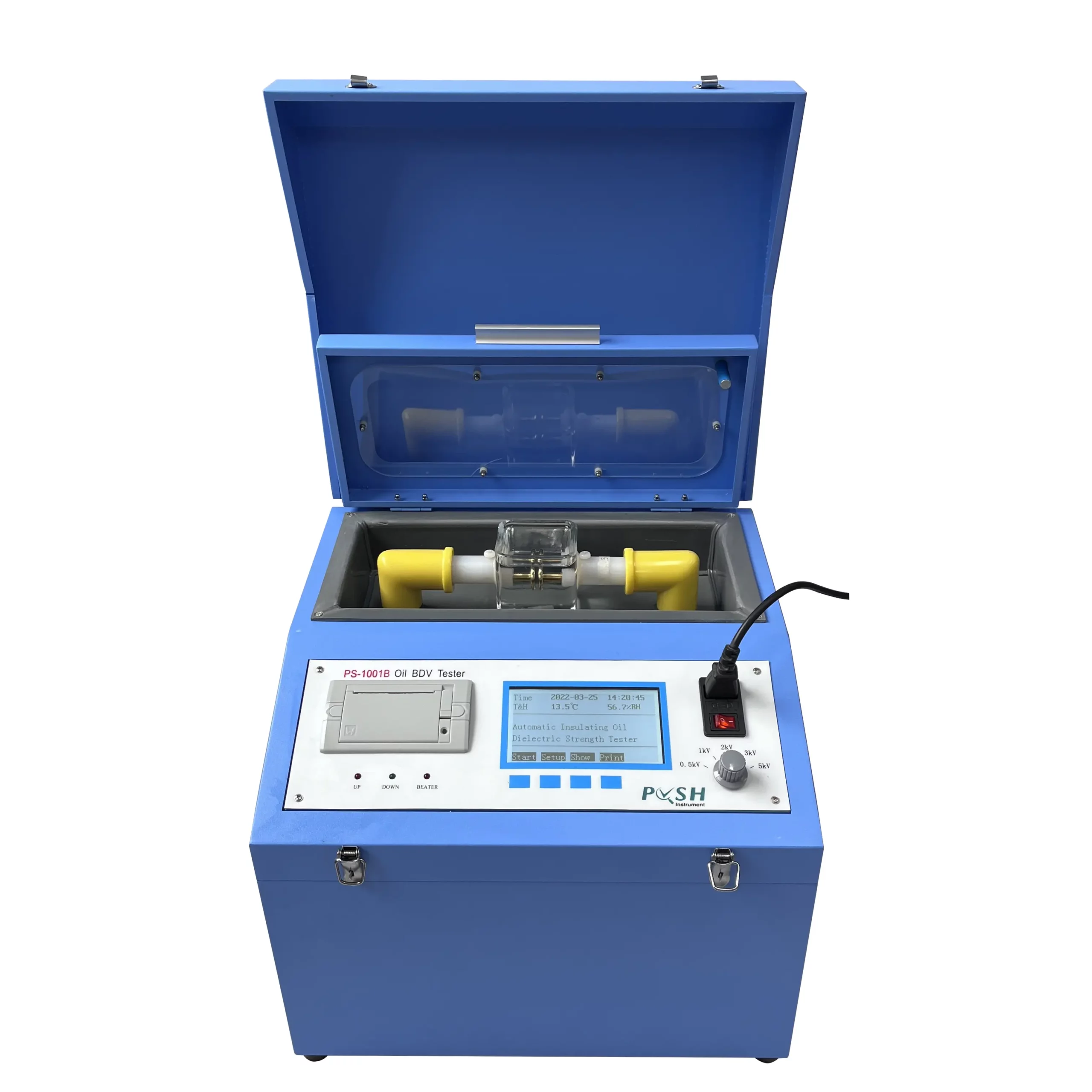
A transformer oil dielectric tester evaluates the level of aging products in transformer oil by conducting tests that assess the oil’s physical and chemical properties, which can indicate the presence and concentration of degradation products.
Here’s how it works:
- Acidity Testing: One method used by transformer oil dielectric testers to evaluate aging products is acidity testing. Aging of transformer oil can lead to the formation of acidic compounds due to oxidation or contamination. Acidity testing measures the pH level or total acidity of the oil, with higher acidity indicating a higher concentration of aging products.
- Furanic Compounds Analysis: Furanic compounds are indicative of thermal and electrical degradation of cellulose insulation in transformers. Transformer oil dielectric testers can analyze the level of furanic compounds, such as furfural, in the oil using techniques such as gas chromatography. Elevated levels of furanic compounds suggest significant degradation of the transformer insulation and aging of the oil.
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Certain gases produced as a result of thermal and electrical breakdown in transformers can serve as indicators of aging and degradation. Transformer oil dielectric testers perform dissolved gas analysis (DGA) to monitor the concentration of gases such as methane, ethylene, and acetylene, which are associated with various stages of insulation aging and degradation.
- Physical and Chemical Properties: Transformer oil dielectric testers may also evaluate the oil’s physical and chemical properties, such as color, transformer oil dielectric tester appearance, viscosity, density, and interfacial tension. Changes in these properties over time can indicate aging and degradation of the oil, as well as the presence of degradation products.
- Interpretation of Results: Based on the results of these tests and analyses, transformer oil dielectric testers can assess the overall level of aging products in the oil and evaluate the condition of the transformer. Elevated levels of acidity, furanic compounds, or certain gases may indicate significant aging and degradation, necessitating further investigation or maintenance actions to prevent potential failures or damage to the transformer.
In summary, a transformer oil dielectric tester evaluates the level of aging products in transformer oil by analyzing various physical, chemical, and electrical properties of the oil, as well as the concentration of specific degradation indicators such as acidity, furanic compounds, and dissolved gases. These tests help assess the condition of the transformer and facilitate timely maintenance or replacement to ensure reliable operation and longevity.